Flagsmith Java SDK
This library can be used with server-side Java, Kotlin and Android applications. The source code for the client is available on Github.
Getting Started
The client library is available from the Central Maven Repository and can be added to your project by many tools:
Maven
Add following dependencies to your project in pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.flagsmith</groupId>
<artifactId>flagsmith-java-client</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
</dependency>
Gradle
implementation 'com.flagsmith:flagsmith-java-client:2.8'
Basic Usage
The SDK is initialised against a single environment within a project on https://flagsmith.com, for example the Development or Production environment. You can find your environment key in the Environment settings page.
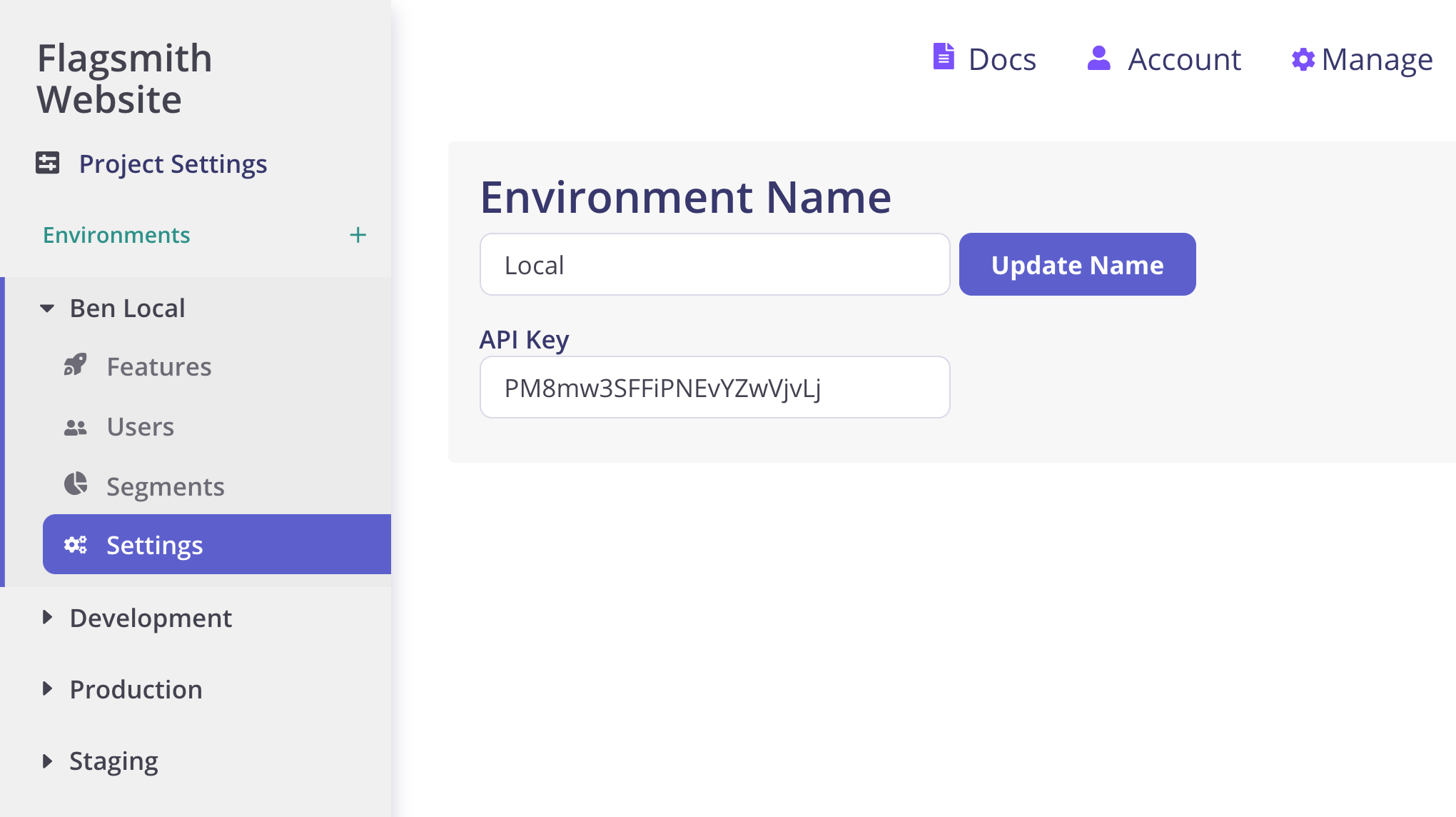
Retrieving feature flags for your project
Sign Up and create an account at https://www.flagsmith.com/
In your application initialise the Flagsmith client with your API key:
FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
.setApiKey("YOUR_ENV_API_KEY")
.build();
To check if a feature flag exists and is enabled:
boolean featureEnabled = flagsmithClient.hasFeatureFlag("my_test_feature");
if (featureEnabled) {
// run the code that executes the enabled feature
} else {
// run the code that doesn't include the feature
}
To get configuration value for a feature flag:
String myRemoteConfig = flagsmithClient.getFeatureFlagValue("my_test_feature");
if (myRemoteConfig != null) {
// run the code that uses the remote config value
} else {
// run the code that doesn't depend on the remote config value
}
Identifying users
Identifying users allows you to target specific users from the Flagsmith dashboard.
To check if feature exists for given a user context:
FeatureUser user = new FeatureUser();
user.setIdentifier("flagsmith_sample_user");
boolean featureEnabled = flagsmithClient.hasFeatureFlag("my_test_feature", user);
if (featureEnabled) {
// run the code that executes the enabled feature for a given user
} else {
// run the code that doesn't include the feature
}
To get the configuration value of a feature flag for a given user context:
String myRemoteConfig = flagsmithClient.getFeatureFlagValue("my_test_feature", user);
if (myRemoteConfig != null) {
// run the code that uses the remote config value
} else {
// run the code that doesn't depend on the remote config value
}
To set user traits:
FeatureUser user = new FeatureUser();
user.setIdentifier(identifier);
FlagsAndTraits flagsAndTraits = flagsmithClient.identifyUserWithTraits(user, Arrays.asList(
new Trait(null, "trait1", "some value1"),
new Trait(null, "trait2", "some value2")));
// Since version 3.0, this method returns a FlagsAndTraits object, from which you can obtain the
// returned flags and / or traits.
List<Trait> traits = flagsAndTraits.getTraits();
List<Flag> flags = flagsAndTraits.getFlags();
To get user traits for a given user context:
List<Trait> userTraits = flagsmithClient.getTraits(user)
if (userTraits != null && userTraits) {
// run the code that expects the user traits
} else {
// run the code that doesn't depend on user traits
}
To get a user trait for a given user context and specific key:
Trait userTrait = flagsmithClient.getTrait(user, "cookies_key");
if (userTrait != null) {
// run the code that uses the user trait
} else {
// run the code that doesn't depend on the user trait
}
Or get the user traits for a given user context and specific keys:
List<Trait> userTraits = flagsmithClient.getTraits(user, "cookies_key", "other_trait");
if (userTraits != null) {
// run the code that uses the user traits
} else {
// run the code doesn't depend on user traits
}
To update the value for user traits for a given user context and specific keys:
Trait userTrait = flagsmithClient.getTrait(user, "cookies_key");
if (userTrait != null) {
// update the value for a user trait
userTrait.setValue("new value");
Trait updated = flagsmithClient.updateTrait(user, userTrait);
} else {
// run the code that doesn't depend on the user trait
}
Flags and Traits
Or get flags and traits for a user in a single call:
FlagsAndTraits userFlagsAndTraits = flagsmithClient.getUserFlagsAndTraits(user);
// get traits
List<Trait> traits = flagsmithClient.getTraits(userFlagsAndTraits, "cookies_key");
// or get a flag value
String featureFlagValue = flagsmithClient.getFeatureFlagValue("font_size", userFlagsAndTraits);
// or get flag enabled
boolean enabled = flagsmithClient.hasFeatureFlag("hero", userFlagsAndTraits);
// see above examples on how to evaluate flags and traits
Override default configuration
By default, the client uses a default configuration. You can override the configuration as follows:
Override just the default API URI with your own:
FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
.setApiKey("YOUR_ENV_API_KEY")
.withApiUrl("http://yoururl.com")
.build();
Override the full configuration with your own
FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
.setApiKey("YOUR_ENV_API_KEY")
.withConfiguration(FlagsmithConfig.newBuilder()
.baseURI("http://yoururl.com")
.connectTimeout(200)
.writeTimeout(5000)
.readTimeout(5000)
.build())
.build();
Logging
Logging is disabled by default. If you would like to enable it then call .enableLogging() on the client builder:
FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
// other configuration as shown above
.enableLogging()
.build();
Flagsmith uses SLF4J and we only implement its API. If your project does not already have SLF4J, then include an implementation, i.e.:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
Custom HTTP Headers
adding custom headers to all HTTP calls:
final HashMap<String, String> customHeaders = new HashMap(){{
put("x-custom-header", "value1");
put("x-my-key", "value2");
}};
FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
// other configuration as shown above
.withCustomHttpHeaders(customHeaders)
.build();
In-Memory Caching
Caching was made available in version 2.6+
If you would like to use in-memory caching, you will need to enable it (it is disabled by default). The main advantage of using in-memory caching is that you can reduce the number of HTTP calls performed to fetch flags.
Flagsmith uses Caffeine, a high performance, near optimal caching library.
If you enable caching on the Flagsmith client without setting any values (as shown below), the following default values will be set for you:
- maxSize(10)
- expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
- project level caching will be disabled by default (i.e. only enabled if you configure a caching key)
// use in-memory caching with Flagsmith defaults as described above
final FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
.setApiKey("YOUR_ENV_API_KEY")
.withConfiguration(FlagsmithConfig
.newBuilder()
.baseURI("http://yoururl.com")
.build())
.withCache(FlagsmithCacheConfig
.newBuilder()
.build())
.build();
If you would like to change the default settings, you can overwrite them by using the available builder methods:
// use in-memory caching with custom configuration
final FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
.setApiKey("YOUR_ENV_API_KEY")
.withConfiguration(FlagsmithConfig
.newBuilder()
.baseURI("http://yoururl.com")
.build())
.withCache(FlagsmithCacheConfig
.newBuilder()
.maxSize(100)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.recordStats()
.enableEnvLevelCaching("some-key-to-avoid-clashing-with-user-identifiers")
.build())
.build();
The user identifier is used as the cache key, this provides granular control over the cache should you require it. If you would like to manipulate the cache:
// this will return null if caching is disabled
final FlagsmithCache cache = flagsmithClient.getCache();
// you can now discard a single or all entries in the cache
cache.invalidate("user-identifier");
// or
cache.invalidateAll();
// get stats (if you have enabled them in the cache configuration, otherwise all values will be zero)
final CacheStats stats = cache.stats();
// check if flags for a user identifier are cached
final FlagsAndTraits flags = cache.getIfPresent("user-identifier");
Since the user identifier is used as the cache key, you need to configure a cache key to enable project level caching. Make sure you select a project level cache key that will never be a user identifier.
// use in-memory caching with Flagsmith defaults and project level caching enabled
final String projectLevelCacheKey = "some-key-to-avoid-clashing-with-user-identifiers";
final FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
.setApiKey("YOUR_ENV_API_KEY")
.withConfiguration(FlagsmithConfig
.newBuilder()
.baseURI("http://yoururl.com")
.build())
.withCache(FlagsmithCacheConfig
.newBuilder()
.enableEnvLevelCaching(projectLevelCacheKey)
.build())
.build();
// if you need to access the cache directly, you can do this:
final FlagsmithCache cache = flagsmithClient.getCache();
// invalidate project level cache
cache.invalidate(projectLevelCacheKey);
// check if project level flags have been cached
final FlagsAndTraits flags = cache.getIfPresent(projectLevelCacheKey);
Default flag/config Values
Evaluating a flag will always return a value, even if the evaluation fails, i.e. the flag does not exist in Flagsmith or
the HTTP call fails. By default, a flag will be evaluated to false for flags and to null for configuration values if
there is an error. If you would like to override this behaviour, you can use the following methods:
final FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
.setApiKey("YOUR_ENV_API_KEY")
.setDefaultFlagPredicate(
(featureFlagName) -> true /* your logic for default flags */
)
.setDefaultFlagValueFunction(
(featureFlagName) ->
"my-new-default-value" /* your logic for default config values */
)
.build();
However, the code above will only be used if the evaluation is for a specific flag name, i.e.
client.getFeatureFlagValue("flag-name") or client.hasFeatureFlag("flag-name"). If you call method
client.getFeatureFlags() and an error occurs, you will get an empty list of flags. If you would like to change this
behaviour, you can configure a default list of flags:
final FlagsmithClient flagsmithClient = FlagsmithClient.newBuilder()
.setApiKey("YOUR_ENV_API_KEY")
.setDefaultFeatureFlags(new HashSet<String>() {{
add("flag-name-1");
add("flag-name-2");
add("flag-name-3");
}})
.build();
Setting default flag names also means that if one of those flags is not configured in the Flagsmith server, it will still be included in the list of flags returned in the example of above.